Digital signatures play a critical role in ensuring the authenticity and integrity of electronic documents and transactions, much like a handwritten signature does in the physical world. They provide a way to verify the identity of the signer and ensure that the content has not been altered. For example, when you sign a contract electronically, a digital signature guarantees that the document remains unchanged and that you are the verified author.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how digital signatures work and the crucial role Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) play in safeguarding them.
Digital Signature Objectives
Digital Signatures fulfill two goals:
- Authenticity: Verify the source from where the data came from
- Integrity: Knowing the data has not been altered or manipulated on the way
Where are digital signatures used for:
Digital signatures have become a critical tool for digital communication, offering a secure and efficient way to authenticate documents and transactions. With widespread adoption, they’ve gained significant legal recognition, serving as a trusted equivalent to handwritten signatures in many jurisdictions.
Example use cases of digital signatures include:
- Electronic Document Signing
- Email signatures
- Retail payments
- Interbank payment systems
- Proving one’s identity with electronic passports and ID-cards
- Website authentication
How Do Digital Signatures Work?
Digital signatures are based on asymmetric cryptography. In asymmetric cryptography, a pair of mathematically related keys is used – one public key and one private key. The keys fulfill different purposes:
- Private Key: For signing purposes
- Public Key: For verification purposes
The private key is owned by the signer and serves as a unique identifier.
The public key is made public – often attached to a certificate – and is used to verify the digital signature of the sender.
For digital signatures, the public and private keys are used in the following ways:
- The sender uses its private key to encrypt the data that needs to be signed, creating a unique hash value.
- The hash value is added to the data – serving as the digital signature.
- The data together with the signature is sent to the receiver.
- The receiver uses the public key to decrypt the signature and compare it to the data.
- If it matches, the receiver knows that the signature is valid.
Verifying Digital Signatures - How Do I know to Trust a Public Key?
Digital signatures and the signing process described above are based on the premise that the receiver trusts the public key and knows that it is from the person he thinks it is. There are two ways of creating trust in public keys:
- Secure key exchange
Key exchange protocols are cryptographic methods to share keys between two parties securely to enable secure communication. - Usage of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
PKI securely manages digital certificates and cryptographic keys, authenticating user identities and ensuring trusted, encrypted communication.
eIDAS Regulation for Digital Signatures
The European Union eIDAS (electronic Identification, Authentication and trust Services) was enacted on 23 July 2014 and put into effect on 1 July 2016. eIDAS mandates stringent guidelines for security protections with digital signatures, electronic transactions, involved bodies, and their embedded practices. In June 2021, the European Commission proposed an update and amendment of the existing eIDAS regulation – commonly referred to as eIDAS 2.0.
The standards mandated by eIDAS work to ensure the integrity of electronic signatures and include the need for many cryptographic protections. However, what is also mandated is the need for sufficiently protecting the cryptographic processes. This is where the security offered by Hardware Security Modules is required to keep critical data, including keys used to confirm digital identities required for signing from falling into the wrong hands. In what follows, we explain the role that HSMs have in digital signing.
Types of digital signatures in eIDAS:
Simple Electronic Signatures
A simple digital signature ensures data integrity and authenticity by using a private key to sign the data and a public key to verify the signature.
Advanced Electronic Signature
Advanced digital signatures offer features like timestamping to ensure long-term validity and legal recognition. They adhere to specific standards, providing greater assurance and reliability.
Qualified Electronic Signature
The most secure electronic signature is the qualified electronic signature, which is an advanced electronic signature that is created by QSCD (qualified signature creation device). This device creates a qualified digital certificate to attest to the authenticity of the digital signature and can only be provided through trust services provided by a trust service provider (TSP). The TSP is responsible for authentication and preservation of the electronic signatures and certificates it creates. A qualified electronic signature offers higher trust and is legally recognized across jurisdictions.
The Role of HSMs in Digital Signing
A Hardware Security Module is a trusted physical computing device that generates, provides, protects and manages cryptographic keys for functions such as encryption and decryption and authentication for the use of applications, identities and databases.
For the use case of digital signatures, the HSM generates the cryptographic key pair and protects the private key in a tamper-proof, hardened environment.
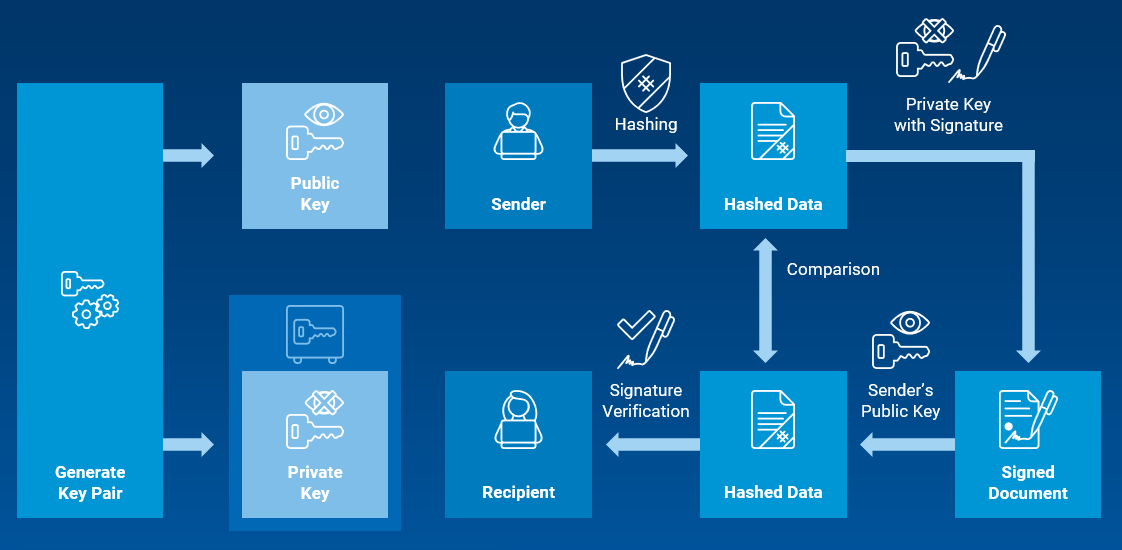
Graphic: The role of public and private keys generated in an HSM for document signing
HSM Functions for Digital Signatures
eIDAS and the Common Criteria Protection Profile – Cryptographic Module for Trust Service Providers specify the security requirements that must be followed for authentication and storage services provided by TSPs. Hardware security modules fall under the specification of a cryptographic module.
HSMs provide the required secure environment that is needed to generate and protect the cryptographic keys used to protect and authenticate sensitive data such as that used in digital signing and authentication of electronic signatures. The module also controls the use of this data for one or more cryptographic services in supporting trust services supplied by TSPs.
Cryptographic modules, such as an HSM that fall under Common Criteria’s Protect Profile and eIDAS Protection Profile (PP) EN 419 221-5 “Cryptographic Module for Trust Services” give TSPs the resources necessary to be in compliance with EU regulations and accepted policies.
HSMs play an important role in digital signing by:
- Generating cryptographic keys using a true random number generator (TRNG)
- Storing sensitive key material in a hardened, tamper-proof environment
- Performing cryptographic operations for encryption and digital signing
- Protecting cryptographic material, including keys and certificates
- Ensuring compliance with key authorization functions for issuing qualified certificates under eIDAS
- Resisting hacking attempts with specialized hardware that guards against side-channel attacks
- Strengthening encryption practices throughout the entire key lifecycle, from generation to disposal
Want to test how an HSM would work for your use case?
Utimaco offers a free HSM simulator for evaluation and integration testing – the perfect way to check if our HSM meets your requirements.